what are the effects of ketoacidosis Pathophysiology and effects of insulin deficiency #insulin
Today, I want to talk about a topic that affects millions of people worldwide: diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). It’s important to understand the symptoms and treatment of this condition, especially if you or someone you know has diabetes. So, let’s dive right in!
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Diabetic ketoacidosis, also known as DKA, is a serious complication that can occur in people with diabetes. It happens when there is a severe lack of insulin in the body, leading to high blood sugar levels.
When the body doesn’t have enough insulin, it starts breaking down fat as an alternative source of energy. This process produces ketones, which are acidic chemicals. As the ketone levels rise in the blood, it becomes more acidic, leading to a condition known as ketoacidosis.
Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Recognizing the symptoms of DKA is crucial for timely treatment. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination
- Abdominal pain and nausea
- Fatigue or weakness
- Fruity breath odor
- Rapid breathing
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- High blood sugar levels
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately. DKA is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to prevent serious complications.
Treating Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 The treatment of DKA usually involves a hospital stay and a multidimensional approach. It focuses on:
The treatment of DKA usually involves a hospital stay and a multidimensional approach. It focuses on:
- Fluid replacement: Intravenous (IV) fluids are administered to rehydrate the body.
- Insulin therapy: Insulin is given to lower blood sugar levels and stop the ketone production.
- Electrolyte replacement: Imbalances in electrolytes, such as potassium and sodium, are corrected through IV medications.
- Treatment of underlying triggers: Infections or other factors that contributed to the development of DKA are identified and treated.
It’s important to remember that prevention is key when it comes to DKA. Proper diabetes management, including regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, taking medications as prescribed, and making necessary lifestyle changes, can help reduce the risk of developing DKA.
Additionally, it’s crucial to educate yourself and others about the warning signs of DKA, especially for those living with diabetes. Prompt recognition and early intervention can save lives.
In conclusion, understanding the symptoms and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is vital for everyone, whether you have diabetes or not. By spreading awareness about this condition, we can contribute to a healthier and more informed society. Remember, knowledge is power!
If you are searching about Pathophysiology and Effects of Insulin Deficiency #Insulin | GrepMed you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Pathophysiology and Effects of Insulin Deficiency #Insulin | GrepMed like Ketosis vs Ketoacidosis: The Difference and dangerous Levels - Medical, SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow and also SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow. Here it is:
Pathophysiology And Effects Of Insulin Deficiency #Insulin | GrepMed
 www.grepmed.compathophysiology deficiency ketoacidosis dka insulin grepmed
www.grepmed.compathophysiology deficiency ketoacidosis dka insulin grepmed
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) | Ketosis Symptoms And Treatment | Diabetes UK
 www.diabetes.org.ukdka ketoacidosis diabetic complications symptome fruity ketosis ketones mellitus anzeichen mantracare abdominal ursachen urine coma occasionally affects
Ketosis Vs Ketoacidosis: The Difference And Dangerous Levels - Medical
 www.medicalestudy.comketoacidosis ketosis vs difference dangerous levels
www.medicalestudy.comketoacidosis ketosis vs difference dangerous levels
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
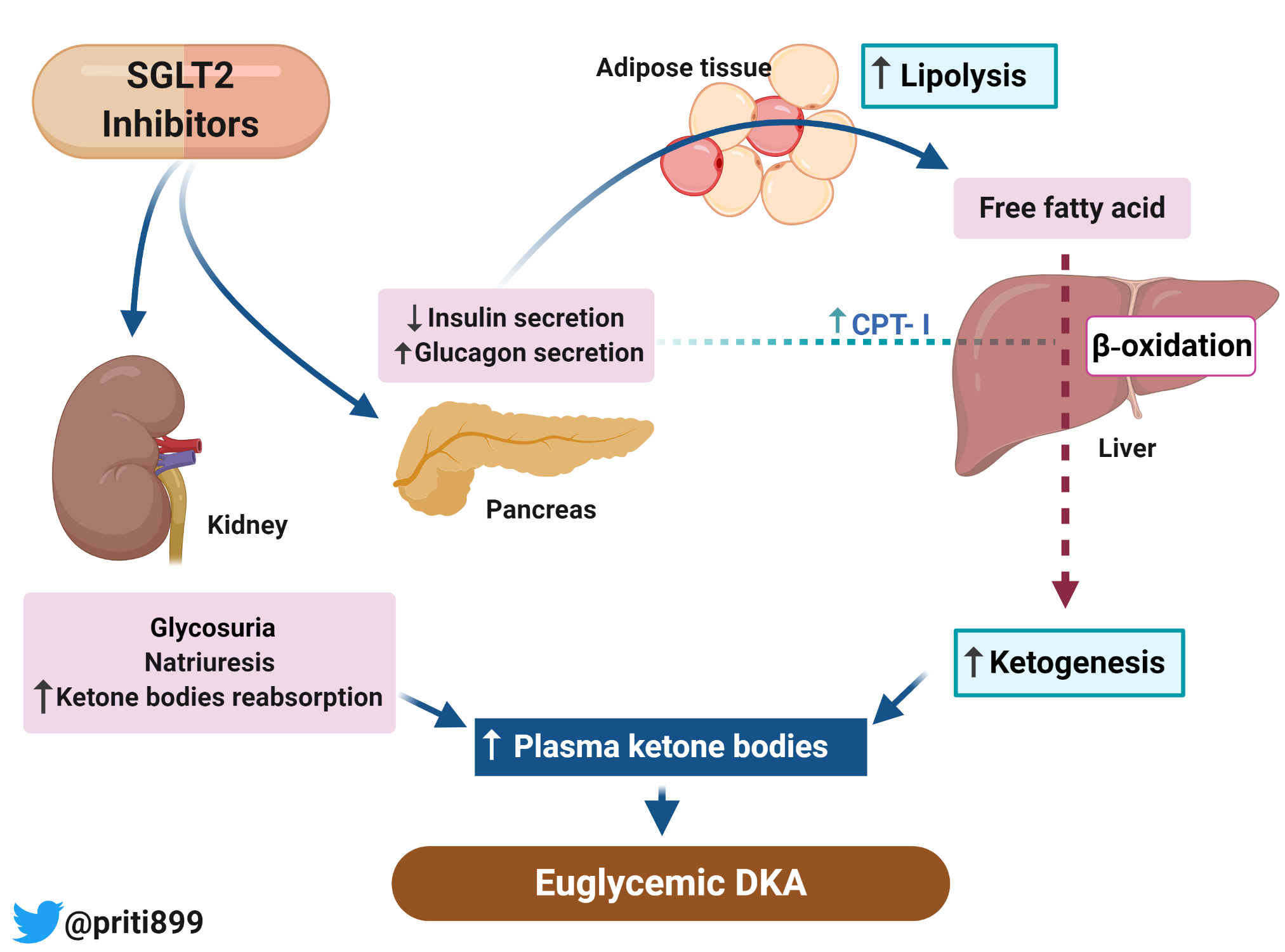 www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Pin On Invokana Side Effects
 www.pinterest.comeffects side info
www.pinterest.comeffects side info
Ketosis vs ketoacidosis: the difference and dangerous levels. Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka). Sglt2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis